The results, by CNPEM researchers, were published in the journal “Scientific Reports” from Nature Group.
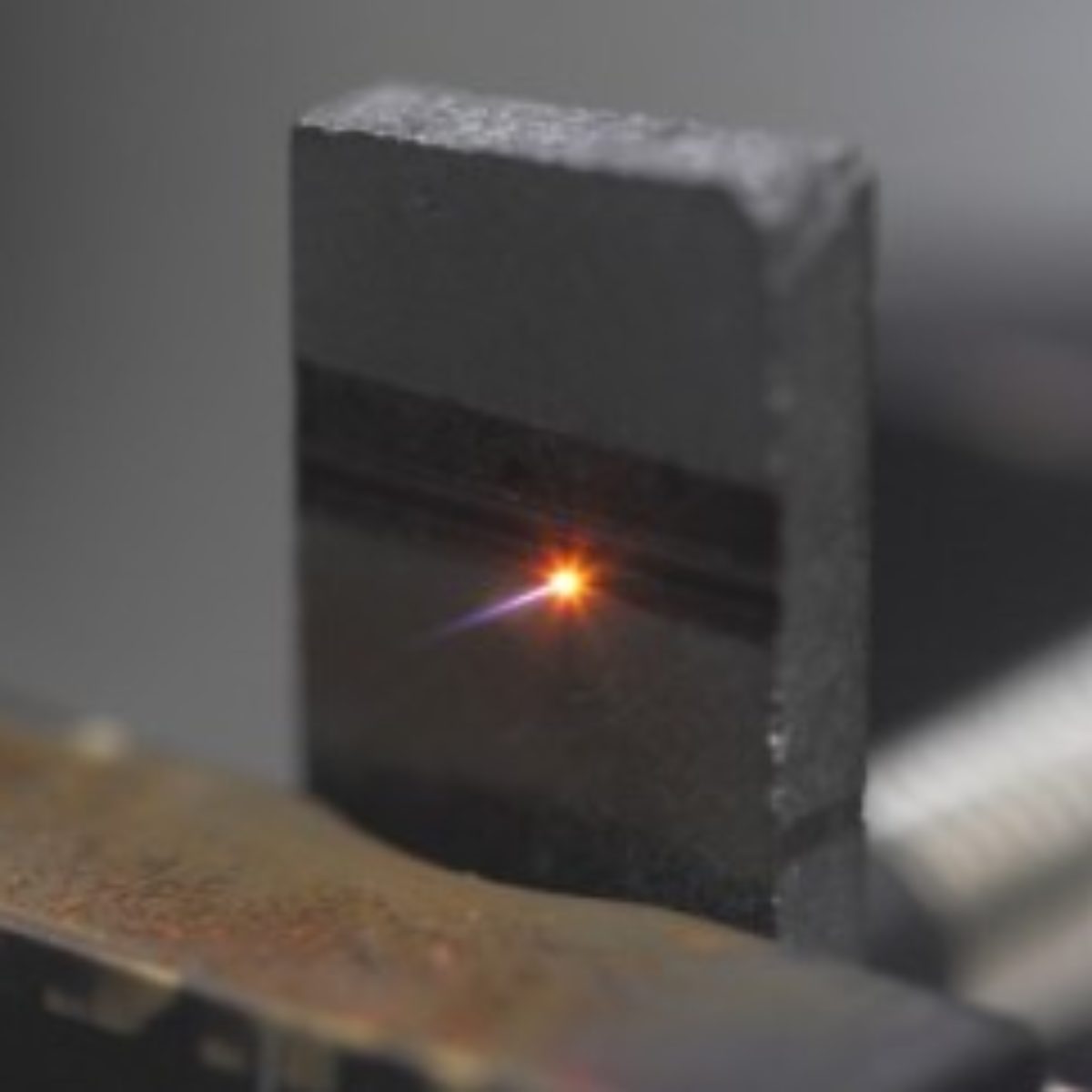
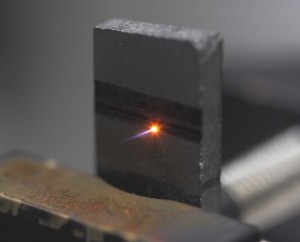 A low-cost way to produce nanostructured diamonds from graphite was developed by researchers from the Brazilian Synchrotron Light Laboratory (LNLS), LNNano (Brazilian Nanotechnology National Laboratory) and Ipen (Nuclear and Energy Research Institute). They used ultrafast laser in order to generate a shock wave, which was able to achieve the pressure and temperature levels necessary to synthesize diamond.
A low-cost way to produce nanostructured diamonds from graphite was developed by researchers from the Brazilian Synchrotron Light Laboratory (LNLS), LNNano (Brazilian Nanotechnology National Laboratory) and Ipen (Nuclear and Energy Research Institute). They used ultrafast laser in order to generate a shock wave, which was able to achieve the pressure and temperature levels necessary to synthesize diamond.
The control processes shown here open new paths to pattern transport from exclusion to preconcentration of charged molecules by selecting the appropriate polymerization strategy and polymerization parameters.
This immediately suggests the hypothesis that, since very few T4SS have been characterized to date, T4SS-mediated bacterial killing may not be restricted to the Xanthomonadaceae family, and may in fact be a more widespread phenomenon.